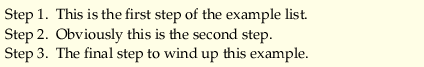Elsarticle.cls: Difference between revisions
| (29 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
[http://tug.ctan.org/tex-archive/macros/latex/contrib/elsarticle/ http://tug.ctan.org]. Please download <code>elsarticle.dtx</code> which is a composite class with documentation and <code>elsarticle.ins</code> which is the LaTeX installer file. When we compile the <code>elsarticle.ins</code> with LaTeX, it provides the class file, <code>elsarticle.cls</code> by stripping off all the documentation from the <code>*.dtx</code> file. The class may be moved or copied to a place, usually, <code>$TEXMF/tex/latex/elsevier/</code>, or a folder which will be read by LaTeX during document compilation. The TeX file database needs updation after moving/copying a class file. Usually, we use commands such as <code>mktexlsr</code> and <code>texhash</code> depending upon the distribution and operating system. | [http://tug.ctan.org/tex-archive/macros/latex/contrib/elsarticle/ http://tug.ctan.org]. Please download <code>elsarticle.dtx</code> which is a composite class with documentation and <code>elsarticle.ins</code> which is the LaTeX installer file. When we compile the <code>elsarticle.ins</code> with LaTeX, it provides the class file, <code>elsarticle.cls</code> by stripping off all the documentation from the <code>*.dtx</code> file. The class may be moved or copied to a place, usually, <code>$TEXMF/tex/latex/elsevier/</code>, or a folder which will be read by LaTeX during document compilation. The TeX file database needs updation after moving/copying a class file. Usually, we use commands such as <code>mktexlsr</code> and <code>texhash</code> depending upon the distribution and operating system. | ||
Currently the latest version of elsarticle.cls (Version | Currently the latest version of elsarticle.cls (Version 3.3) is available only in this wiki page. CTAN and author resources pages at Elsevier will be updated as soon as possible. | ||
==Usage== | ==Usage== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
where the <code>options</code> can be the following: | where the <code>options</code> can be the following: | ||
; <code>preprint</code>: default option which format the document for submission to Elsevier journals. Along with this option < | ; <code>preprint</code>: default option which format the document for submission to Elsevier journals. Along with this option <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\date{Custom date}</syntaxhighlight> can be provided which will be printed in preprint line in footer. | ||
; <code>nopreprintline</code>: Suppresses the preprint line in the footer of the first page including the date. | ; <code>nopreprintline</code>: Suppresses the preprint line in the footer of the first page including the date. | ||
; <code>review</code>: similar to the <code>preprint</code> option, but increases the baselineskip to facilitate an easier review process. | ; <code>review</code>: similar to the <code>preprint</code> option, but increases the baselineskip to facilitate an easier review process. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
\biboptions{longnamesfirst,angle,semicolon} | \biboptions{longnamesfirst,angle,semicolon} | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
; <code>number</code>: numbered citation style. Extra options can be loaded with < | ; <code>number</code>: numbered citation style. Extra options can be loaded with <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\biboptions</syntaxhighlight> command. | ||
; <code>sort&compress</code>: sorts and compresses the numbered citations. For example, citation [1,2,3] will become [1-3]. | ; <code>sort&compress</code>: sorts and compresses the numbered citations. For example, citation [1,2,3] will become [1-3]. | ||
; <code>longtitle</code>: if front matter is unusually long, use this option to split the title page across pages with the correct placement of title and author footnotes in the first page. | ; <code>longtitle</code>: if front matter is unusually long, use this option to split the title page across pages with the correct placement of title and author footnotes in the first page. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | ||
\begin{frontmatter} | \begin{frontmatter} | ||
\title{This is a specimen title\tnoteref{t1,t2}} | \title{This is a specimen $a_b$ title\tnoteref{t1,t2}} | ||
\tnotetext[t1]{This document is the results of the research | \tnotetext[t1]{This document is the results of the research | ||
project funded by the National Science Foundation.} | project funded by the National Science Foundation.} | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
\author[1]{ | \author[1]{J.K. Krishnan\corref{cor1}% | ||
\fnref{fn1}} | \fnref{fn1}} | ||
\ead{ | \ead{jkk@example.in} | ||
\author[1,2]{Han Thane\fnref{fn2}} | |||
\ead{han@different.edu} | |||
\author[3]{T. Rafeeq\fnref{fn1,fn3}} | |||
\ead[url]{www.nowhere.com} | |||
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author} | |||
\fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.} | |||
\fntext[fn2]{Another author footnote, this is a very long footnote and | |||
it should be a really long footnote. But this footnote is not yet | |||
sufficiently long enough to make two lines of footnote text.} | |||
\fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.} | |||
\affiliation[1]{organization={Department of Physics, | |||
J.K. Institute of Science}, | |||
addressline={Jawahar Nagar}, | |||
city={Trivandrum}, | |||
% citysep={}, % Uncomment if no comma needed between city and postcode | |||
postcode={695013}, | |||
state={Kerala}, | |||
country={India}} | |||
\ | \affiliation[2]{organization={World Scientific University}, | ||
addressline={Street 29}, | |||
postcode={1011 NX}, | |||
postcodesep={}, | |||
city={Amsterdam}, | |||
country={The Netherlands}} | |||
\ | \affiliation[3]{organization={University of Intelligent Studies}, | ||
addressline={Street 15}, | |||
city={Jabaldesh}, | |||
postcode={825001}, | |||
state={Orissa}, | |||
country={India}} | |||
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author} | \cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author} | ||
| Line 106: | Line 136: | ||
lines of footnote text.} | lines of footnote text.} | ||
\fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.} | \fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.} | ||
. . . | . . . | ||
| Line 119: | Line 142: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Output of | Output of another TeX source which was coded as above will look like as the following: | ||
[[Image: | <table frame="box"> | ||
<tr><td>[[Image:Els-fm1.png|650px]]</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
;Output of the footnotes and footer part will be as below: | |||
<table frame="box"> | |||
<tr><td>[[Image:Els-fm1a.png|650px]]</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
Most of the commands such as < | Most of the commands such as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\title</syntaxhighlight>, <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\author</syntaxhighlight>, <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\address</syntaxhighlight> are self-explanatory. Various components are linked to each other by a | ||
label–reference mechanism; for instance, title footnote is linked to the title with a footnote mark generated by referring to the < | label–reference mechanism; for instance, title footnote is linked to the title with a footnote mark generated by referring to the <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\label</syntaxhighlight> string of the <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\tnotetext</syntaxhighlight>. We have used similar commands such as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\tnoteref</syntaxhighlight> (to link the title note to the title), <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\corref</syntaxhighlight> (to link the corresponding author text to the corresponding author); <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\fnref</syntaxhighlight> (to link the footnote text to the relevant author names). TeX needs two compilations to resolve the footnote marks in the preamble part. Given below are the syntax of various note marks and note texts. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | ||
\tnoteref{<label(s)>} | \tnoteref{<label(s)>} | ||
| Line 139: | Line 167: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
where <code><label(s)></code> can be either one or more comma delimited | where <code><label(s)></code> can be either one or more comma delimited | ||
label strings. The optional arguments to the < | label strings. The optional arguments to the <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\author</syntaxhighlight> | ||
command holds the ref label(s) of the address(es) to which the author | command holds the ref label(s) of the address(es) to which the author | ||
is affiliated while each < | is affiliated while each <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\address</syntaxhighlight> command can have an | ||
optional argument of a label. In the same manner, | optional argument of a label. In the same manner, | ||
< | <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\tnotetext</syntaxhighlight>, <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\fntext</syntaxhighlight>, <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\cortext</syntaxhighlight> | ||
will have optional arguments as their respective labels and note text | will have optional arguments as their respective labels and note text | ||
as their mandatory argument. | as their mandatory argument. | ||
| Line 150: | Line 178: | ||
author affiliation. | author affiliation. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | ||
\author{ | |||
\author{J.K. Krishnan\corref{cor1}% | |||
\fnref{fn1}} | \fnref{fn1}} | ||
\ead{ | \ead{jkk@example.in} | ||
\affiliation{organization={Department of Physics, | |||
J.K. Institute of Science}, | |||
addressline={Jawahar Nagar}, | |||
city={Trivandrum}, | |||
% citysep={}, % Uncomment if no comma needed between city and postcode | |||
postcode={695013}, | |||
\author{ | state={Kerala}, | ||
\ead{ | country={India}} | ||
\author{Han Thane\fnref{fn2}} | |||
\ead{han@different.edu} | |||
\affiliation{organization={World Scientific University}, | |||
addressline={Street 29}, | |||
\author{ | postcode={1011 NX}, | ||
\ead[url]{www. | postcodesep={}, | ||
city={Amsterdam}, | |||
country={The Netherlands}} | |||
\author{T. Rafeeq\fnref{fn1,fn3}} | |||
\ead[url]{www.nowhere.com} | |||
\affiliation{organization={University of Intelligent Studies}, | |||
addressline={Street 15}, | |||
city={Jabaldesh}, | |||
postcode={825001}, | |||
state={Orissa}, | |||
country={India}} | |||
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author} | \cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author} | ||
\fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.} | \fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.} | ||
| Line 186: | Line 220: | ||
The output of the above TeX sources will look like the following: | The output of the above TeX sources will look like the following: | ||
[[Image: | <table frame="box"> | ||
<tr><td>[[Image:Els-fm2.png|650px]]</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
;Output of the footnotes and footer part will be as below: | |||
<table frame="box"> | |||
<tr><td>[[Image:Els-fm1a.png|650px]]</td></tr> | |||
</table> | |||
The front matter part has further environments such as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\begin{abstract} . . . \end{abstract}</syntaxhighlight> and <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\begin{keyword} ... \end{keyword}</syntaxhighlight> which contain the abstract and keywords respectively. | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | |||
manner: | \begin{abstract} | ||
In this work we demonstrate the formation of a new type of polariton on | |||
the interface between a cuprous oxide slab and a polystyrene | |||
micro-sphere placed on the slab. ..... | |||
\end{abstract} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
Keywords can be marked up in the following manner: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | ||
\begin{keyword} | \begin{keyword} | ||
| Line 196: | Line 249: | ||
\end{keyword} | \end{keyword} | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Each keyword shall be separated by a < | Each keyword shall be separated by a <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\sep</syntaxhighlight> command. MSC classifications shall be provided in the keyword environment with the commands <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\MSC</syntaxhighlight>. <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\MSC</syntaxhighlight> accepts an optional argument to accommodate future revisions. e.g. <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\MSC[2008]</syntaxhighlight>. The default is 2000. | ||
===Specimen of a title page coding=== | ===Specimen of a title page coding=== | ||
| Line 223: | Line 276: | ||
first page.} | first page.} | ||
\author[1]{ | \author[1]{J.K. Krishnan\corref{cor1}% | ||
\fnref{fn1}} | \fnref{fn1}} | ||
\ead{ | \ead{jkk@example.in} | ||
\author[2]{ | \author[1,2]{Han Thane\fnref{fn2}} | ||
\ead{ | \ead{han@different.edu} | ||
\author[3]{ | \author[3]{T. Rafeeq\fnref{fn1,fn3}} | ||
\ead[url]{www. | \ead[url]{www.nowhere.com} | ||
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author} | |||
\fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.} | |||
\fntext[fn2]{Another author footnote, this is a very long footnote and | |||
it should be a really long footnote. But this footnote is not yet | |||
sufficiently long enough to make two lines of footnote text.} | |||
\fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.} | |||
\affiliation[1]{organization={Department of Physics, | |||
J.K. Institute of Science}, | |||
addressline={Jawahar Nagar}, | |||
city={Trivandrum}, | |||
% citysep={}, % Uncomment if no comma needed between city and postcode | |||
postcode={695013}, | |||
state={Kerala}, | |||
country={India}} | |||
\affiliation[2]{organization={World Scientific University}, | |||
addressline={Street 29}, | |||
postcode={1011 NX}, | |||
postcodesep={}, | |||
city={Amsterdam}, | |||
country={The Netherlands}} | |||
\affiliation[3]{organization={University of Intelligent Studies}, | |||
addressline={Street 15}, | |||
city={Jabaldesh}, | |||
postcode={825001}, | |||
state={Orissa}, | |||
country={India}} | |||
\begin{abstract} | \begin{abstract} | ||
| Line 275: | Line 331: | ||
Although quadrupole excitons (QE) in cuprous oxide crystals are good | Although quadrupole excitons (QE) in cuprous oxide crystals are good | ||
candidates for BEC... See section \ref{sec1}. | candidates for BEC... See section \ref{sec1}. | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
===Other useful environments in the front matter=== | |||
Graphical abstract and Highlights are to be given within {frontmatter} environment. | |||
====Graphical abstract==== | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | |||
\begin{graphicalabstract} | |||
\includegraphics{graphicalabstract.png} | |||
\end{graphicalabstract} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
;Highlights | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | |||
\begin{highlights} | |||
\item This is the highlight point of this article. | |||
\item This is the highlight point of this article. | |||
\item This is the highlight point of this article. | |||
\end{highlights} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==Floats== | ==Floats== | ||
Figures may be included using the command, < | Figures may be included using the command, <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\includegraphics</syntaxhighlight> in combination with or without its several options to further control graphics. <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\includegraphics</syntaxhighlight> is provided by <code>graphic[s,x].sty</code> which is part of any standard LaTeX distribution. | ||
<code>graphicx.sty</code> is loaded by default. LaTeX accepts figures in the postscript format while pdfLaTeX accepts <code>*.pdf</code>, <code>*.mps</code> (metapost), <code>*.jpg</code> and <code>*.png</code> formats. pdfLaTeX does not accept graphic files in the postscript format. | <code>graphicx.sty</code> is loaded by default. LaTeX accepts figures in the postscript format while pdfLaTeX accepts <code>*.pdf</code>, <code>*.mps</code> (metapost), <code>*.jpg</code> and <code>*.png</code> formats. pdfLaTeX does not accept graphic files in the postscript format. | ||
| Line 284: | Line 362: | ||
==Theorem and theorem-like environments== | ==Theorem and theorem-like environments== | ||
<code>elsarticle.cls</code> provides a few shortcuts to format theorems and theorem-like environments with ease. In all commands the options that are used with the < | <code>elsarticle.cls</code> provides a few shortcuts to format theorems and theorem-like environments with ease. In all commands the options that are used with the <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\newtheorem</syntaxhighlight> command will work exactly in the same manner. <code>elsarticle.cls</code> provides three commands to format theorem or theorem-like environments: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | ||
\newtheorem{thm}{Theorem} | \newtheorem{thm}{Theorem} | ||
| Line 293: | Line 371: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
The < | The <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\newtheorem</syntaxhighlight> command formats a theorem in LaTeX's default style with italicized font, bold font for theorem heading and theorem number at the right hand side of the theorem heading. It also optionally accepts an argument which will be printed as an extra heading in parentheses. The following text will show you how some text enclosed in <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\begin{thm} . . . \end{thm}</syntaxhighlight> will look like. | ||
[[Image:Els3.png|700px]] | [[Image:Els3.png|700px]] | ||
The < | The <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\newdefinition</syntaxhighlight> command is the same in all respects as its <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\newtheorem</syntaxhighlight> counterpart except that the font shape is roman instead of italic. Both <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\newdefinition</syntaxhighlight> and <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\newtheorem</syntaxhighlight> commands automatically define counters for the environments defined. See the output of <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\begin{rmk} . . . \end{rmk}</syntaxhighlight> which is given below. | ||
| Line 304: | Line 382: | ||
The < | The <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\newproof</syntaxhighlight> command defines proof environments with upright font shape. No counters are defined. See the output of <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\begin{pot} . . . \end{pot}</syntaxhighlight> which is given below. | ||
| Line 313: | Line 391: | ||
==Enumerated and Itemized Lists== | ==Enumerated and Itemized Lists== | ||
<code>elsarticle.cls</code> provides extended list processing macros which makes the usage a bit more user friendly than the default LaTeX list macros. With an optional argument to the < | <code>elsarticle.cls</code> provides extended list processing macros which makes the usage a bit more user friendly than the default LaTeX list macros. With an optional argument to the <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\begin{enumerate}</syntaxhighlight> command, you can change the list counter type and its attributes. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="latex"> | ||
\begin{enumerate}[1.] | \begin{enumerate}[1.] | ||
| Line 360: | Line 438: | ||
==Cross-references== | ==Cross-references== | ||
In electronic publications, articles may be internally hyperlinked. Hyperlinks are generated from proper cross-references in the article. For example, the words | In electronic publications, articles may be internally hyperlinked. Hyperlinks are generated from proper cross-references in the article. For example, the words | ||
<code>Fig. 1</code> will never be more than a simple text, whereas the proper cross-reference < | <code>Fig. 1</code> will never be more than a simple text, whereas the proper cross-reference <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\ref{tiger}</syntaxhighlight> may be turned into a hyperlink to the figure itself: <code>Fig. 1</code>. In the same way, the words <code>Ref. [1]</code> will fail to turn into a hyperlink; the proper cross-reference is <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\cite{Knuth96}</syntaxhighlight>. Cross-referencing is possible in LaTeX for sections, subsections, formulae, figures, tables, and literature references. | ||
==Mathematical symbols and formulae== | ==Mathematical symbols and formulae== | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
Many physical/mathematical science authors require more mathematical symbols than the few that are provided in standard LaTeX. A useful package for | Many physical/mathematical science authors require more mathematical symbols than the few that are provided in standard LaTeX. A useful package for | ||
additional symbols is the <code>amssymb</code> package, developed by the American Mathematical Society. This package includes such oft-used symbols as < | additional symbols is the <code>amssymb</code> package, developed by the American Mathematical Society. This package includes such oft-used symbols as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\lesssim</syntaxhighlight> for <math>\lesssim</math> and <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\gtrsim</syntaxhighlight> for <math>\gtrsim</math> or <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\hbar</syntaxhighlight> for <math>\gtrsim</math>. Note that your TeX system should have the <code>msam</code> and <code>msbm</code> fonts installed. If you need only a few symbols, such as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\Box</synaxhighlight> for <math>\Box</math>, you might try the package <code>latexsym</code>. | ||
--> | --> | ||
Many physical/mathematical science authors require more mathematical symbols than the few that are provided in standard LaTeX. A useful package for | Many physical/mathematical science authors require more mathematical symbols than the few that are provided in standard LaTeX. A useful package for | ||
additional symbols is the <code>amssymb</code> package, developed by the American Mathematical Society. This package includes such oft-used symbols as < | additional symbols is the <code>amssymb</code> package, developed by the American Mathematical Society. This package includes such oft-used symbols as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\lesssim</syntaxhighlight>, <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\gtrsim</syntaxhighlight> or <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\hbar</syntaxhighlight>. Note that your TeX system should have the <code>msam</code> and <code>msbm</code> fonts installed. If you need only a few symbols, such as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\Box</syntaxhighlight>, you might try the package <code>latexsym</code>. | ||
<table border="1" cellspacing="3" cellpadding="3"> | <table border="1" cellspacing="3" cellpadding="3"> | ||
| Line 383: | Line 461: | ||
Three bibliographic style files (*.bst) are provided — <code>elsarticle-num.bst</code>, <code>elsarticle-num-names.bst</code> and <code>elsarticle-harv.bst</code> — the first one for the numbered scheme, the second for the numbered with new options of natbib.sty and the last one for the author–year scheme. | Three bibliographic style files (*.bst) are provided — <code>elsarticle-num.bst</code>, <code>elsarticle-num-names.bst</code> and <code>elsarticle-harv.bst</code> — the first one for the numbered scheme, the second for the numbered with new options of natbib.sty and the last one for the author–year scheme. | ||
In the LaTeX literature, references are listed in the <code>thebibliography</code> environment. Each reference is a < | In the LaTeX literature, references are listed in the <code>thebibliography</code> environment. Each reference is a <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\bibitem</syntaxhighlight> and each <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\bibitem</syntaxhighlight> is identified by a label, by which it can be cited in the text: <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\bibitem[Elson et al.(1996)]{ESG96}</syntaxhighlight> is cited as <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\citet{ESG96}</syntaxhighlight>. In connection with cross-referencing and possible future hyperlinking it is not a good idea to collect more than one literature item in one <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\bibitem</syntaxhighlight>. The so-called Harvard or author–year style of referencing is enabled by the LaTeX package <code>natbib</code>. With this package the literature can be cited as follows: | ||
* Parenthetical: < | * Parenthetical: <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\citep{WB96}</syntaxhighlight> produces (Wettig & Brown, 1996). | ||
* Textual: < | * Textual: <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\citet{ESG96}</syntaxhighlight> produces Elson et al. (1996). | ||
* An affix and part of a reference: < | * An affix and part of a reference: <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\citep[e.g.][Ch. 2]{Gea97}</syntaxhighlight> produces (e.g. Governato et al., 1997, Ch. 2). | ||
In the numbered scheme of citation, < | In the numbered scheme of citation, <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\cite{<label>}</syntaxhighlight> is used, since <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\citep</syntaxhighlight> or <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\citet</syntaxhighlight> has no relevance in the numbered scheme. <code>natbib</code> package is loaded by <code>elsarticle.cls</code> with numbers as default options. You can change this to the author–year or harvard scheme by adding option <code>authoryear</code> in the class loading command. If you want to use more options of the <code>natbib</code> package, you can do so with the <syntaxhighlight lang="latex" inline>\biboptions</syntaxhighlight> command, which is described in the section [http://support.river-valley.com/wiki/index.php?title=Elsarticle.cls#Usage Usage]. For details of various options of the <code>natbib</code> package, please take a look at the natbib documentation, which is part of any standard LaTeX installation. | ||
==Final print== | ==Final print== | ||
| Line 400: | Line 478: | ||
Following is the first page of a typical single column article. | Following is the first page of a typical single column article. | ||
<table frame="box"> | |||
[[Image: | <tr><td>[[Image:Els-1p.png|675px]]</td></tr> | ||
</table> | |||
Model 1+ and 3+ will have the same look and feel in the typeset copy when presented in this document. This is also the case with the double column 3+ and 5+ journal article pages. The only difference will be the wider text width of higher models. Therefore we will look at the different portions of a typical single column journal page and that of a double column article in the final format. | Model 1+ and 3+ will have the same look and feel in the typeset copy when presented in this document. This is also the case with the double column 3+ and 5+ journal article pages. The only difference will be the wider text width of higher models. Therefore we will look at the different portions of a typical single column journal page and that of a double column article in the final format. | ||
| Line 407: | Line 486: | ||
Following is the first page of a typical double column article. | Following is the first page of a typical double column article. | ||
<table frame="box"> | |||
[[Image: | <tr><td>[[Image:Els-5p.png|675px]]</td></tr> | ||
</table> | |||
==Displayed equations and double column journals== | ==Displayed equations and double column journals== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:49, 17 December 2022
[LaTeX Tutorial] [Elsarticle - CAS] [FAQ - elsarticle.cls] [Model-wise bibliographic style files]
Introduction
elsarticle.cls is a thoroughly rewritten document class
for formatting LaTeX submissions to Elsevier journals.
This class uses the environments and commands defined in the LaTeX kernel
without any change in the signature so that clashes with other
contributed LaTeX packages such as hyperref.sty,
preview-latex.sty, etc. will be minimal.
elsarticle.cls is primarily built upon the default
article.cls. This class depends on the following packages
for its proper functioning:
pifont.styfor openstar in the title footnotes;natbib.styfor citation processing;geometry.styfor margin settings;fleqn.clofor left aligned equations;graphicx.styfor graphics inclusion;txfonts.styoptional font package, if the document is to be formatted with Times and compatible math fonts;hyperref.styoptional packages if hyperlinking is required in the document.
All the above packages are part of any standard LaTeX installation.
Therefore, the users need not be bothered about downloading any
extra packages. Furthermore, users are free to make use of AMS
math packages such as amsmath.sty, amsthm.sty,
amssymb.sty, amsfonts.sty, etc., if they want to. All
these packages work in tandem with elsarticle.cls without
any problems.
Major Differences
Following are the major differences between elsarticle.cls and its predecessor package, elsart.cls:
elsarticle.clsis built uponarticle.clswhileelsart.clsis not.elsart.clsredefines many of the commands in the LaTeX classes/kernel, which can possibly cause surprising clashes with other contributed LaTeX packages;- provides preprint document formatting by default, and optionally formats the document as per the final style of models
1+,3+and5+of Elsevier journals; - some easier ways for formatting
listandtheoremenvironments are provided while people can still useamsthm.stypackage; natbib.styis the main citation processing package which can comprehensively handle all kinds of citations and works perfectly withhyperref.styin combination withhypernat.sty;- long title pages are processed correctly in preprint and final formats.
Installation
The package is available at author resources page at Elsevier.
It can also be found in any of the nodes of the Comprehensive TeX Archive Network (CTAN), one of the primary nodes being
http://tug.ctan.org. Please download elsarticle.dtx which is a composite class with documentation and elsarticle.ins which is the LaTeX installer file. When we compile the elsarticle.ins with LaTeX, it provides the class file, elsarticle.cls by stripping off all the documentation from the *.dtx file. The class may be moved or copied to a place, usually, $TEXMF/tex/latex/elsevier/, or a folder which will be read by LaTeX during document compilation. The TeX file database needs updation after moving/copying a class file. Usually, we use commands such as mktexlsr and texhash depending upon the distribution and operating system.
Currently the latest version of elsarticle.cls (Version 3.3) is available only in this wiki page. CTAN and author resources pages at Elsevier will be updated as soon as possible.
Usage
The class should be loaded with the command:
\documentclass[<options>]{elsarticle}
where the options can be the following:
preprint- default option which format the document for submission to Elsevier journals. Along with this option
\date{Custom date}can be provided which will be printed in preprint line in footer. nopreprintline- Suppresses the preprint line in the footer of the first page including the date.
review- similar to the
preprintoption, but increases the baselineskip to facilitate an easier review process. 1p- formats the article to the look and feel of the final format of model 1+ journals. This is always of single column style.
3p- formats the article to the look and feel of the final format of model 3+ journals. If the journal is a two column model, use
twocolumnoption in combination. 5p- formats for model 5+ journals. This is always of two column style.
authoryear- author–year citation style of
natbib.sty. If you want to add extra options ofnatbib.sty, you may use the options as comma delimited strings as arguments to the\biboptionscommand. An example would be:
\biboptions{longnamesfirst,angle,semicolon}
number- numbered citation style. Extra options can be loaded with
\biboptionscommand. sort&compress- sorts and compresses the numbered citations. For example, citation [1,2,3] will become [1-3].
longtitle- if front matter is unusually long, use this option to split the title page across pages with the correct placement of title and author footnotes in the first page.
times- loads
txfonts.sty, if available in the system to use Times and compatible math fonts.
- All options of
article.clscan be used with this document class. - The default options loaded are
a4paper,10pt,oneside,onecolumnandpreprint.
Front matter
There are two types of front matter coding —
- each author is connected to an affiliation with a footnote marker, and hence all authors are grouped together and the affiliations follow;
- authors with the same affiliation are grouped together and the relevant affiliation follows this group. An example coding of the first type is provided below:
\begin{frontmatter}
\title{This is a specimen $a_b$ title\tnoteref{t1,t2}}
\tnotetext[t1]{This document is the results of the research
project funded by the National Science Foundation.}
\tnotetext[t2]{The second title footnote which is a longer
text matter to fill through the whole text width and
overflow into another line in the footnotes area of the
first page.}
\author[1]{J.K. Krishnan\corref{cor1}%
\fnref{fn1}}
\ead{jkk@example.in}
\author[1,2]{Han Thane\fnref{fn2}}
\ead{han@different.edu}
\author[3]{T. Rafeeq\fnref{fn1,fn3}}
\ead[url]{www.nowhere.com}
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author}
\fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.}
\fntext[fn2]{Another author footnote, this is a very long footnote and
it should be a really long footnote. But this footnote is not yet
sufficiently long enough to make two lines of footnote text.}
\fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.}
\affiliation[1]{organization={Department of Physics,
J.K. Institute of Science},
addressline={Jawahar Nagar},
city={Trivandrum},
% citysep={}, % Uncomment if no comma needed between city and postcode
postcode={695013},
state={Kerala},
country={India}}
\affiliation[2]{organization={World Scientific University},
addressline={Street 29},
postcode={1011 NX},
postcodesep={},
city={Amsterdam},
country={The Netherlands}}
\affiliation[3]{organization={University of Intelligent Studies},
addressline={Street 15},
city={Jabaldesh},
postcode={825001},
state={Orissa},
country={India}}
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author}
\fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.}
\fntext[fn2]{Another author footnote, this is a very long
footnote and it should be a really long footnote. But this
footnote is not yet sufficiently long enough to make two
lines of footnote text.}
\fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.}
. . .
. . .
\end{frontmatter}
Output of another TeX source which was coded as above will look like as the following:
 |
- Output of the footnotes and footer part will be as below
 |
Most of the commands such as \title, \author, \address are self-explanatory. Various components are linked to each other by a
label–reference mechanism; for instance, title footnote is linked to the title with a footnote mark generated by referring to the \label string of the \tnotetext. We have used similar commands such as \tnoteref (to link the title note to the title), \corref (to link the corresponding author text to the corresponding author); \fnref (to link the footnote text to the relevant author names). TeX needs two compilations to resolve the footnote marks in the preamble part. Given below are the syntax of various note marks and note texts.
\tnoteref{<label(s)>}
\corref{<label(s)>}
\fnref{<label(s)>}
\tnotetext[<label>]{<title note text>}
\cortext[<label>]{<corresponding author note text>}
\fntext[<label>]{<author footnote text>}
where <label(s)> can be either one or more comma delimited
label strings. The optional arguments to the \author
command holds the ref label(s) of the address(es) to which the author
is affiliated while each \address command can have an
optional argument of a label. In the same manner,
\tnotetext, \fntext, \cortext
will have optional arguments as their respective labels and note text
as their mandatory argument.
The following example code provides the markup of the second type of author affiliation.
\author{J.K. Krishnan\corref{cor1}%
\fnref{fn1}}
\ead{jkk@example.in}
\affiliation{organization={Department of Physics,
J.K. Institute of Science},
addressline={Jawahar Nagar},
city={Trivandrum},
% citysep={}, % Uncomment if no comma needed between city and postcode
postcode={695013},
state={Kerala},
country={India}}
\author{Han Thane\fnref{fn2}}
\ead{han@different.edu}
\affiliation{organization={World Scientific University},
addressline={Street 29},
postcode={1011 NX},
postcodesep={},
city={Amsterdam},
country={The Netherlands}}
\author{T. Rafeeq\fnref{fn1,fn3}}
\ead[url]{www.nowhere.com}
\affiliation{organization={University of Intelligent Studies},
addressline={Street 15},
city={Jabaldesh},
postcode={825001},
state={Orissa},
country={India}}
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author}
\fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.}
\fntext[fn2]{Another author footnote; this is a very long footnote and
it should be a really long footnote. But this footnote is not
sufficiently long enough to make two lines of footnote text.}
\fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.}
The output of the above TeX sources will look like the following:
 |
- Output of the footnotes and footer part will be as below
 |
The front matter part has further environments such as \begin{abstract} . . . \end{abstract} and \begin{keyword} ... \end{keyword} which contain the abstract and keywords respectively.
\begin{abstract}
In this work we demonstrate the formation of a new type of polariton on
the interface between a cuprous oxide slab and a polystyrene
micro-sphere placed on the slab. .....
\end{abstract}
Keywords can be marked up in the following manner:
\begin{keyword}
quadruple exiton \sep polariton \sep WGM
\end{keyword}
Each keyword shall be separated by a \sep command. MSC classifications shall be provided in the keyword environment with the commands \MSC. \MSC accepts an optional argument to accommodate future revisions. e.g. \MSC[2008]. The default is 2000.
Specimen of a title page coding
Following is the specimen of a title page coding.
\documentclass[preprint,1p,12pt]{elsarticle}
\journal{Nuclear Physics B}
\begin{document}
\begin{frontmatter}
\title{This is a specimen title\tnoteref{t1,t2}}
\tnotetext[t1]{This document is a collaborative effort.}
\tnotetext[t2]{The second title footnote which is longer
than the first one and with an intention to fill
in up more than one line while formatting.}
\title{This is a specimen title\tnoteref{t1,t2}}
\tnotetext[t1]{This document is the results of the research
project funded by the National Science Foundation.}
\tnotetext[t2]{The second title footnote which is a longer
text matter to fill through the whole text width and
overflow into another line in the footnotes area of the
first page.}
\author[1]{J.K. Krishnan\corref{cor1}%
\fnref{fn1}}
\ead{jkk@example.in}
\author[1,2]{Han Thane\fnref{fn2}}
\ead{han@different.edu}
\author[3]{T. Rafeeq\fnref{fn1,fn3}}
\ead[url]{www.nowhere.com}
\cortext[cor1]{Corresponding author}
\fntext[fn1]{This is the first author footnote.}
\fntext[fn2]{Another author footnote, this is a very long footnote and
it should be a really long footnote. But this footnote is not yet
sufficiently long enough to make two lines of footnote text.}
\fntext[fn3]{Yet another author footnote.}
\affiliation[1]{organization={Department of Physics,
J.K. Institute of Science},
addressline={Jawahar Nagar},
city={Trivandrum},
% citysep={}, % Uncomment if no comma needed between city and postcode
postcode={695013},
state={Kerala},
country={India}}
\affiliation[2]{organization={World Scientific University},
addressline={Street 29},
postcode={1011 NX},
postcodesep={},
city={Amsterdam},
country={The Netherlands}}
\affiliation[3]{organization={University of Intelligent Studies},
addressline={Street 15},
city={Jabaldesh},
postcode={825001},
state={Orissa},
country={India}}
\begin{abstract}
In this work we demonstrate the formation of a new type of polariton on
the interface between a cuprous oxide slab and a polystyrene
micro-sphere placed on the slab. .....
\end{abstract}
\begin{keyword}
quadruple exciton \sep polariton \sep WGM
\end{keyword}
\end{frontmatter}
\section{Introduction}\label{sec1}
Although quadrupole excitons (QE) in cuprous oxide crystals are good
candidates for BEC... See section \ref{sec1}.
Other useful environments in the front matter
Graphical abstract and Highlights are to be given within {frontmatter} environment.
Graphical abstract
\begin{graphicalabstract}
\includegraphics{graphicalabstract.png}
\end{graphicalabstract}
- Highlights
\begin{highlights}
\item This is the highlight point of this article.
\item This is the highlight point of this article.
\item This is the highlight point of this article.
\end{highlights}
Floats
Figures may be included using the command, \includegraphics in combination with or without its several options to further control graphics. \includegraphics is provided by graphic[s,x].sty which is part of any standard LaTeX distribution.
graphicx.sty is loaded by default. LaTeX accepts figures in the postscript format while pdfLaTeX accepts *.pdf, *.mps (metapost), *.jpg and *.png formats. pdfLaTeX does not accept graphic files in the postscript format.
The table environment is handy for marking up tabular material. If users want to use multirow.sty, array.sty, etc., to fine control/enhance the tables, they are welcome to load any package of their choice and elsarticle.cls will work in combination with all loaded packages.
Theorem and theorem-like environments
elsarticle.cls provides a few shortcuts to format theorems and theorem-like environments with ease. In all commands the options that are used with the \newtheorem command will work exactly in the same manner. elsarticle.cls provides three commands to format theorem or theorem-like environments:
\newtheorem{thm}{Theorem}
\newtheorem{lem}[thm]{Lemma}
\newdefinition{rmk}{Remark}
\newproof{pf}{Proof}
\newproof{pot}{Proof of Theorem \ref{thm2}}
The \newtheorem command formats a theorem in LaTeX's default style with italicized font, bold font for theorem heading and theorem number at the right hand side of the theorem heading. It also optionally accepts an argument which will be printed as an extra heading in parentheses. The following text will show you how some text enclosed in \begin{thm} . . . \end{thm} will look like.
The \newdefinition command is the same in all respects as its \newtheorem counterpart except that the font shape is roman instead of italic. Both \newdefinition and \newtheorem commands automatically define counters for the environments defined. See the output of \begin{rmk} . . . \end{rmk} which is given below.
The \newproof command defines proof environments with upright font shape. No counters are defined. See the output of \begin{pot} . . . \end{pot} which is given below.
Users can also make use of amsthm.sty which will override all the default definitions described above.
Enumerated and Itemized Lists
elsarticle.cls provides extended list processing macros which makes the usage a bit more user friendly than the default LaTeX list macros. With an optional argument to the \begin{enumerate} command, you can change the list counter type and its attributes.
\begin{enumerate}[1.]
\item The enumerate environment starts with an optional argument `1.', so that the item counter will be suffixed by a period.
\item If you provide a closing parenthesis to the number in the optional argument, the output will have closing parentheses for all the item counters.
\item You can use `(a)' for alphabetical counter and '(i)' for roman counter.
\begin{enumerate}[a)]
\item Another level of list with alphabetical counter.
\item One more item before we start another.
\begin{enumerate}[(i)]
\item This item has roman numeral counter.
\item Another one before we close the third level.
\end{enumerate}
\item Third item in second level.
\end{enumerate}
\item All list items conclude with this step.
\end{enumerate}
The typeset copy of the above source code is given below:
Furthermore, the enhanced list environment allows one to prefix a string-like `step' to all the item numbers. Take a look at the example below:
\begin{enumerate}[Step 1.]
\item This is the first step of the example list.
\item Obviously this is the second step.
\item The final step to wind up this example.
\end{enumerate}
The typeset copy of the above source code is given below:
Cross-references
In electronic publications, articles may be internally hyperlinked. Hyperlinks are generated from proper cross-references in the article. For example, the words
Fig. 1 will never be more than a simple text, whereas the proper cross-reference \ref{tiger} may be turned into a hyperlink to the figure itself: Fig. 1. In the same way, the words Ref. [1] will fail to turn into a hyperlink; the proper cross-reference is \cite{Knuth96}. Cross-referencing is possible in LaTeX for sections, subsections, formulae, figures, tables, and literature references.
Mathematical symbols and formulae
Many physical/mathematical science authors require more mathematical symbols than the few that are provided in standard LaTeX. A useful package for
additional symbols is the amssymb package, developed by the American Mathematical Society. This package includes such oft-used symbols as \lesssim, \gtrsim or \hbar. Note that your TeX system should have the msam and msbm fonts installed. If you need only a few symbols, such as \Box, you might try the package latexsym.
Another point which would require the authors' attention is the breaking up of long equations. When you use elsarticle.cls for formatting your submissions in the preprint mode, the document is formatted in single column style with a text width of 384pt or 5.3in. When this document is formatted for final print and if the journal happens to be a double column journal, the text width will be reduced to 224pt for 3+ double column and 5+ journals respectively. All the nifty fine-tuning in equation breaking done by the author goes to waste in such cases. Therefore, authors are requested to check this problem by typesetting their submissions in the final format as well just to see if their equations are broken at the appropriate places, by changing appropriate options in the document class loading command, which is explained in the section Usage. This allows authors to fix any equation breaking problem before submission for publication. elsarticle.cls supports formatting the author submission in different types of final format. This is further discussed in
the section Final print.
Bibliography
Three bibliographic style files (*.bst) are provided — elsarticle-num.bst, elsarticle-num-names.bst and elsarticle-harv.bst — the first one for the numbered scheme, the second for the numbered with new options of natbib.sty and the last one for the author–year scheme.
In the LaTeX literature, references are listed in the thebibliography environment. Each reference is a \bibitem and each \bibitem is identified by a label, by which it can be cited in the text: \bibitem[Elson et al.(1996)]{ESG96} is cited as \citet{ESG96}. In connection with cross-referencing and possible future hyperlinking it is not a good idea to collect more than one literature item in one \bibitem. The so-called Harvard or author–year style of referencing is enabled by the LaTeX package natbib. With this package the literature can be cited as follows:
- Parenthetical:
\citep{WB96}produces (Wettig & Brown, 1996). - Textual:
\citet{ESG96}produces Elson et al. (1996). - An affix and part of a reference:
\citep[e.g.][Ch. 2]{Gea97}produces (e.g. Governato et al., 1997, Ch. 2).
In the numbered scheme of citation, \cite{<label>} is used, since \citep or \citet has no relevance in the numbered scheme. natbib package is loaded by elsarticle.cls with numbers as default options. You can change this to the author–year or harvard scheme by adding option authoryear in the class loading command. If you want to use more options of the natbib package, you can do so with the \biboptions command, which is described in the section Usage. For details of various options of the natbib package, please take a look at the natbib documentation, which is part of any standard LaTeX installation.
Final print
The authors can format their submission to the page size and margins of their preferred journal. elsarticle provides four class options for the same.
But it does not mean that using these options you can emulate the exact page layout of the final print copy.
1p- 1+ journals with a text area of 384pt × 562pt or 13.5cm × 19.75cm or 5.3in × 7.78in, single column style only.
3p- 3+ journals with a text area of 468pt × 622pt or 16.45cm × 21.9cm or 6.5in × 8.6in, single column style.
twocolumn- should be used along with
3poption if the journal is 3+ with the same text area as above, but double column style. 5p- 5+ with a text area of 522pt × 682pt or 18.35cm × 24cm or 7.22in × 9.45in, double column style only.
Following is the first page of a typical single column article.
 |
Model 1+ and 3+ will have the same look and feel in the typeset copy when presented in this document. This is also the case with the double column 3+ and 5+ journal article pages. The only difference will be the wider text width of higher models. Therefore we will look at the different portions of a typical single column journal page and that of a double column article in the final format.
Following is the first page of a typical double column article.
 |
Displayed equations and double column journals
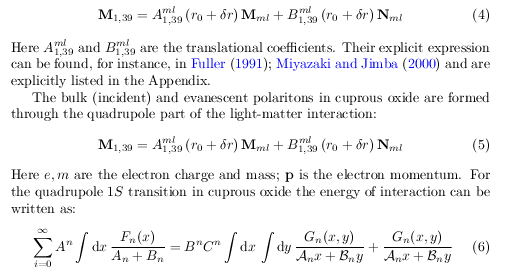
Many Elsevier journals print their text in two columns. Since the preprint layout uses a larger line width than such columns, the formulae are too wide for the line width in print. Here is an example of an equation (see equation 6) which is perfect in a single column preprint format:
When this document is typeset for publication in a model 3+ journal with double columns, the equation will overlap the second column text matter if the equation is not broken at the appropriate location.
The typesetter will try to break the equation which need not necessarily be to the liking of the author or as happens, the typesetter's break point may be semantically incorrect. Therefore, authors may check their submissions for the incidence of such long equations and break the equations at the correct places so that the final typeset copy will be as they wish.
Download the elsarticle packages
The following files are available for download:
- elsarticle.cls, the class file
- elsarticle-num.bst, bibtex style file for numerical references
- elsarticle-harv.bst, bibtex style file for name-year references
- elsarticle-num-names.bst, bibtex style file for numerical references also allowing name-year citations
- elsarticle-template-num.tex, template file for numerical references
- elsarticle-template-harv.tex, template file for name-year references
- elsarticle-v3.3-ELS.zip, the above files in a single zip file. Also it contains the source files for generating elsdoc-print.pdf.
- elsarticle-model-wise-bst.zip. This archive contains model-wise bibliographic bst files and specimen templates.
- logos.zip, the logos.
Contact
Please write to elsarticle@stmdocs.in for any help, feedbacks or suggestions.